Table of Contents
ToggleThe Role of Kidneys:
Kidneys are remarkable organs, resembling two bean-shaped structures located on either side of the spine, below the ribcage. Their primary function is to filter waste products, excess salts, and fluids from the bloodstream, creating urine which is then excreted from the body. Additionally, kidneys regulate vital elements like electrolytes and maintain a healthy balance of fluids. These functions are crucial for overall bodily health, as they ensure the blood stays clean and maintains a stable chemical composition.
Understanding Stage 5 Kidney Failure:

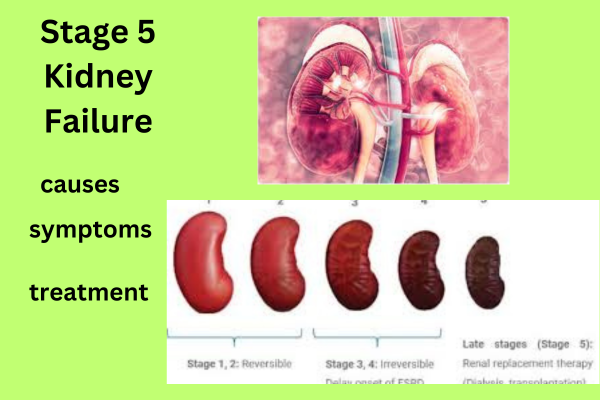
Stage 5 Kidney Failure represents the most advanced and severe form of kidney disease. In this stage, the kidneys have experienced a significant decline in function, with a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) below 15 mL/min/1.73 m². To put it simply, the kidneys have lost nearly all of their ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood, leading to a buildup of toxins and harmful substances. As a result, the body suffers from a range of complications, affecting various organ systems.
Key Features of Stage 5 Kidney Failure: Understanding Severity
Stage 5 kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a serious medical condition characterized by severe impairment of kidney function. At this stage, the kidneys have lost almost all of their ability to filter waste, excess fluid and electrolytes from the blood. This results in the accumulation of toxins in the body, leading to symptoms and complications. Key features of stage 5 kidney failure are:
**1. Significant impairment of kidney function:
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) below 15 mL/min/1.73 m²: GFR measures the rate at which the kidneys filter blood. In stage 5 kidney failure, the GFR falls below 15 mL/min/1.73 m², indicating a significant decline in kidney function.
**2. Accumulation of waste products:
Toxins and waste build-up: The kidneys are unable to effectively remove waste products such as urea and creatinine from the blood. As a result, these toxins accumulate in the body, causing a range of symptoms.
**3. Fluid and electrolyte imbalances:
Failure to regulate fluid levels: The kidneys lose their ability to balance fluids, leading to fluid retention, swelling (edema), and high blood pressure.
Electrolyte Imbalance: The kidneys play an important role in regulating electrolytes such as sodium, potassium and calcium. In stage 5 kidney failure, these electrolytes become imbalanced, affecting various body functions.
**4. Systemic symptoms and complications:
Fatigue: Accumulation of toxins in the bloodstream leads to extreme fatigue and lack of energy.
Shortness of breath: Fluid accumulation in the lungs causes difficulty in breathing.
Nausea and Vomiting: Uremic toxins affect the gastrointestinal system, causing nausea and vomiting.
Pruritus: Accumulation of waste products in the skin causes severe itching.
Urine changes: Urine may be dark, foamy or bloody, indicating kidney failure.
Loss of appetite: Metallic taste in the mouth and uremic toxins suppress appetite, leading to weight loss.
**5. The need for renal replacement therapy:
Dialysis: Most people with stage 5 kidney failure need dialysis, a medical procedure that artificially filters the blood to remove waste and excess fluids.
Kidney Transplant: Kidney transplant becomes a viable option for suitable candidates. A healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor is surgically transplanted to replace the failing kidney, offering a long-term solution.
Understanding these key features is critical for patients, caregivers, and health care providers. Appropriate management, including dialysis, transplant evaluation, and symptom control, is essential to enhance the quality of life of individuals experiencing stage 5 kidney failure.
Causes of Stage 5 Kidney Failure: Unraveling the Underlying Factors
Stage 5 kidney failure, or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a critical condition where the kidneys lose their ability to function effectively. Several underlying causes can lead to this advanced stage of kidney disease. Understanding these causes is important as it helps in prevention, early detection and proper management. Here’s a closer look at the key factors in stage 5 kidney failure:
**1. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD):
High blood pressure (hypertension): Long-term, uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease. Over time, this can progress to stage 5 kidney failure.
Diabetes: Diabetes, especially when not well managed, can cause significant damage to the kidneys. Elevated blood sugar levels impair the kidney’s filtration system, leading to progressive kidney disease and ultimately ESRD.
**2. Glomerulonephritis:
Inflammation of Glomeruli: Glomerulonephritis is a group of diseases that cause inflammation of the small filter glomeruli in the kidney. Inflammatory processes can impair kidney function and, in severe cases, lead to kidney failure.
**3. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD):
Genetic disorders: Polycystic kidney disease is an inherited condition characterized by the development of cysts within the kidneys. These cysts can gradually replace healthy kidney tissue, impair kidney function, and eventually lead to ESRD.
**4. Infection:
Chronic kidney infections: Persistent and severe kidney infections, such as pyelonephritis, can scar and damage kidney tissue, affecting their ability to function effectively.
**5. Autoimmune diseases:
Lupus Nephritis: Lupus is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, including the kidneys. Lupus nephritis specifically affects the kidneys, causing inflammation and kidney damage.
IgA Nephropathy: IgA nephropathy is a kidney disorder where the immune system deposits an antibody called immunoglobulin A (IgA) in the kidneys. It can cause inflammation and disrupt normal kidney function.
**6. Other reasons:
Obstructive disorders: Conditions such as kidney stones, tumors, or an enlarged prostate can obstruct the urethra, leading to kidney damage if left untreated.
Nephrotic syndrome: This syndrome, characterized by proteinuria (excessive protein in the urine), can result from various underlying diseases and can damage the kidneys over time.
Recognizing the underlying causes of stage 5 kidney failure is critical for both prevention and early intervention. Regular health check-ups, management of underlying health conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of reaching this critical stage of kidney disease. Additionally, early diagnosis and appropriate medical care can help effectively manage underlying causes, potentially slowing the progression of kidney disease and improving overall quality of life for those at risk.
Causes of Stage 5 Kidney Failure: Unraveling the Underlying Factors

Stage 5 kidney failure, or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), causes a variety of symptoms due to severely impaired kidney function. It is very important to understand these symptoms as they indicate an urgent need for medical attention and intervention. Here is a detailed look at the common symptoms associated with stage 5 kidney failure:
**1. Fatigue and weakness:
Cause: A build-up of toxins in the body, leading to overall weakness and extreme fatigue.
Effect: Patients may feel lethargic, lacking energy even for basic daily activities.
**2. Swelling (Oedema):
Cause: Failure of the kidneys to regulate fluid balance, leading to fluid retention.
Effect: Swelling occurs in the ankles, legs and face, causing the affected areas to appear puffy and puffy.
**3. Shortness of breath:
Cause: Accumulation of excess fluid in the lungs due to kidney failure.
Effect: Patients experience shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or when lying down.
**4. Nausea and vomiting:
Cause: Accumulation of uremic toxins in the bloodstream.
Effect: Persistent nausea and vomiting, often severe, leading to loss of appetite and malnutrition.
5. Scabies (itching):
Cause: Accumulation of toxins, minerals and waste products in the skin.
Effect: The skin becomes severely itchy, causing pain and discomfort.
**6. Changes in urine:
Cause: Failure of the kidneys to filter waste products, leading to abnormal changes in urine.
Effect: Urine may be dark, foamy, bloody, or smelly. Patients may also experience increased or decreased urinary frequency.
**7. High blood pressure (hypertension):
Cause: Failure of the kidneys to control blood pressure due to disruption of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Effect: High blood pressure can further damage the kidneys and increase the risk of cardiovascular complications.
**8. Loss of appetite and weight loss:
Cause: Uremic toxins affect the taste buds and produce a metallic taste in the mouth.
Implications: Patients may have a decreased appetite, leading to unintentional weight loss and malnutrition.
9. Difficulty sleeping:
Cause: Discomfort due to swelling, itching, or difficulty breathing can disrupt sleep patterns.
Impact: Patients may experience insomnia or poor quality sleep, which can further affect overall health.
It is important to recognize these symptoms, as they indicate advanced kidney failure and the need for immediate medical attention. Patients experiencing any of these symptoms, especially those with underlying conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure, should seek immediate medical advice. Timely intervention, such as dialysis or a kidney transplant, can significantly improve the quality of life of people with stage 5 kidney failure.
Treatment of stage 5 renal failure: management of a critical condition
Stage 5 kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), requires comprehensive and ongoing medical care to manage its complications and enhance the patient’s quality of life. Treatment options for stage 5 kidney failure usually include a combination of treatments designed to address the underlying cause, relieve symptoms, and replace lost kidney function. Here is a detailed description of the treatment options:
**1. Dialysis:
Purpose: Dialysis is a life-saving procedure that mimics kidney function by removing waste, excess fluid, and electrolytes from the blood.
Types:
Hemodialysis: Blood is filtered externally through a dialyzer machine, which cleans the blood before it is returned to the body.
Peritoneal dialysis: A special fluid is injected into the abdominal cavity, where it absorbs waste products from the blood vessels into the peritoneum and is then flushed out.
Frequency: Dialysis is usually done several times a week, and each session lasts several hours.
**2. Kidney transplant:
Objective: Kidney transplantation is the most effective long-term treatment for stage 5 kidney failure. A healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor replaces the failing kidney, restoring kidney function.
Eligibility: Patients are thoroughly screened to determine their suitability for transplantation, considering factors such as overall health, compatibility, and absence of contraindications.
Immunosuppressants: Transplant recipients must take immunosuppressants to prevent rejection of the transplanted kidney. Regular follow-up with health care providers is critical to monitor kidney function and adjust medications as needed.
**3. Medicines:
Purpose: Medications are prescribed to manage symptoms, control blood pressure, and treat complications from kidney failure.
Common medications:
Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents (ESAs): Stimulate red blood cell production to treat anemia, a common complication of kidney failure.
Phosphate binder: Controls high levels of phosphorus in the blood, which can lead to bone problems and cardiovascular disease.
Blood pressure medications: help control blood pressure, reduce stress on the heart and kidneys.
Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements: Maintain bone health and prevent bone diseases associated with kidney failure.
**4. Changes in diet:
Objective: A balanced diet helps manage symptoms and reduce stress on the kidneys.
Restrictions: Patients are often advised to limit potassium, phosphorus and sodium intake. Furthermore, the amount of protein can be adjusted according to the needs of the individual.
**5. Lifestyle changes:
Objective: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce symptoms and contribute to overall well-being.
Quit smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels, worsens kidney problems and increases the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity can increase high blood pressure and diabetes, two leading causes of kidney failure.
Regular exercise: Physical activity supports cardiovascular health and overall well-being, which benefits both physical and mental well-being.
**6. Psychological support:
Objective: Coping with the challenges of stage 5 kidney failure can be emotionally and mentally taxing. Psychological support, including counseling and support groups, can provide patients and their families with valuable resources for managing stress and maintaining a positive outlook.
Treatment for stage 5 kidney failure is multifaceted, including medical interventions, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing support. Early diagnosis, adherence to medical advice and a strong support system are essential to effectively manage this critical condition and improve the patient’s quality of life. Regular communication with health care providers, along with a proactive approach to self-care, plays an important role in the overall well-being of people living with stage 5 kidney failure.
Conclusion:
In summary, the management of stage 5 kidney failure requires a multidisciplinary approach that includes ophthalmologists, dietitians, mental health professionals, and support networks. Regular monitoring, adherence to medical advice, and a positive mindset can significantly improve the quality of life of people living with ESRD. Additionally, raising awareness about kidney health, promoting early diagnosis, and research advocacy are important steps in the global effort to combat this debilitating condition.
By promoting a collective understanding of the causes, symptoms and treatment options of stage 5 kidney failure, society can offer compassion, support and resources to those affected. Through continued research, clinical development, and community education, the journey of those battling this condition can be made easier, hope can be fostered, and outcomes can be improved for a healthier future.